Balancing Your Patients’ Needs™
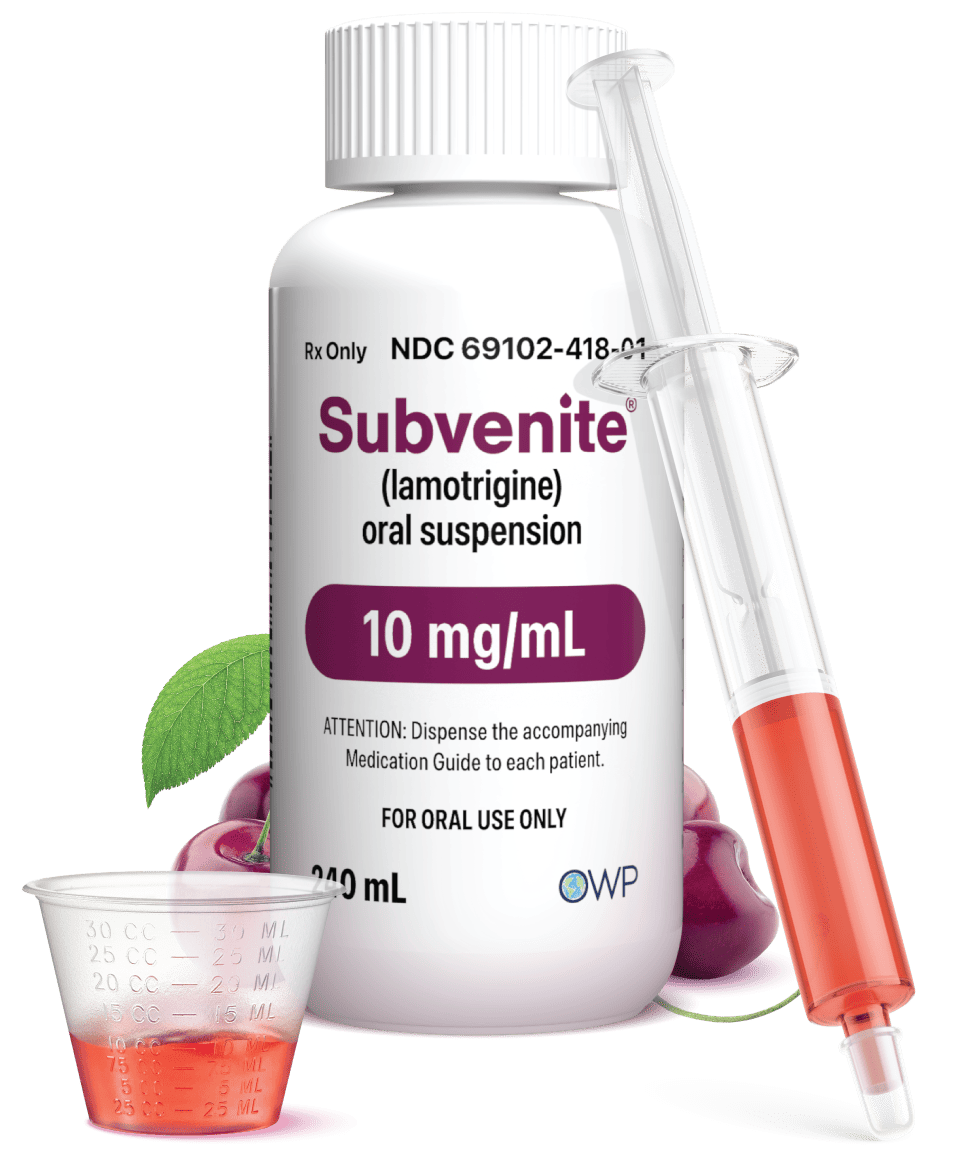
The ONLY FDA-Approved Ready-to-Use* lamotrigine oral suspension
*Shake well before use


For What Conditions is SUBVENITE® Oral Suspension Indicated?
SUBVENITE is indicated for:
Epilepsy—adjunctive therapy in patients aged 2 years and older:
- partial-onset seizures
- primary generalized tonic-clonic (PGTC) seizures
- generalized seizures of Lennox-Gastaut syndrome.
Epilepsy—monotherapy in patients aged 16 years and older: Conversion to monotherapy in patients with partial-onset seizures who are receiving treatment with carbamazepine, phenytoin, phenobarbital, primidone, or valproate as the single antiepileptic drug.
Bipolar disorder: Maintenance treatment of bipolar I disorder to delay the time to occurrence of mood episodes in patients treated for acute mood episodes with standard therapy.
Why Choose SUBVENITE® Oral Suspension?
SUBVENITE® (lamotrigine) Oral Suspension may help fulfill an unmet medical need by providing:
- Individualized dosing during titration of lamotrigine
- Flexibility as patients progress in their treatment path
- No compounding or crushing needed
- Available at most retail pharmacies within 24 hours
Convenient Savings Program for Cost Affordability
Eligible Commercial Patients pay as little as $0 with the SUBVENITE Patient Savings Card.*
*Subject to eligibility restrictions apply
An Opportunity to Help Others
A portion of the profits from the sale of SUBVENITE® helps support the humanitarian work of ROW Global Health ↗, an organization dedicated to help bring training, diagnostics, and treatment to under-resourced communities around the world.

Talk to your healthcare provider to see if SUBVENITE® (lamotrigine) Oral Suspension may be right for you.
If you are a patient currently taking lamotrigine or you are interested in learning more about SUBVENITE®, please visit the SUBVENITE® Oral Suspension Patient Page.
*Lamictal® is a registered trademark of GlaxoSmithKline, Inc. †Terms and conditions apply; see lamotriginestarterkits.com/savings-program. 1https://www.goodrx.com/lamictal?dosage=49-tablets-of-25mg-and-100mg-orange&form=kit&label_override=Lamictal&quantity=1. 2Conn VS, et. al. Current Medical Research and Opinion. 2015;31:1;145-160. 3Gutierrez PM, et. al. Journal of Psychiatric Practice. 2017;23:5;320–327. 4Peterson GM, et. al. Epilepsia. 1984;25:4;412-417.
For general questions or inquiries please contact us at: info@owppharma.com. For SUBVENITE (lamotrigine) Oral Suspension medical questions please contact us at: medinfo.OWP@apcerls.com or call 1-800-273-6729 and follow the prompts for medical information requests. For SUBVENITE (lamotrigine) Oral Suspension safety-related concerns please contact us at: safety.OWP@apcerls.com or call 1-800-273-6729 and follow the prompts for medical adverse events reporting.
SUBOS1013V1 11/25

